| Home | Science | Detector | Collaboration | Publications & Talks | Events | LSM | internal |
Science
|
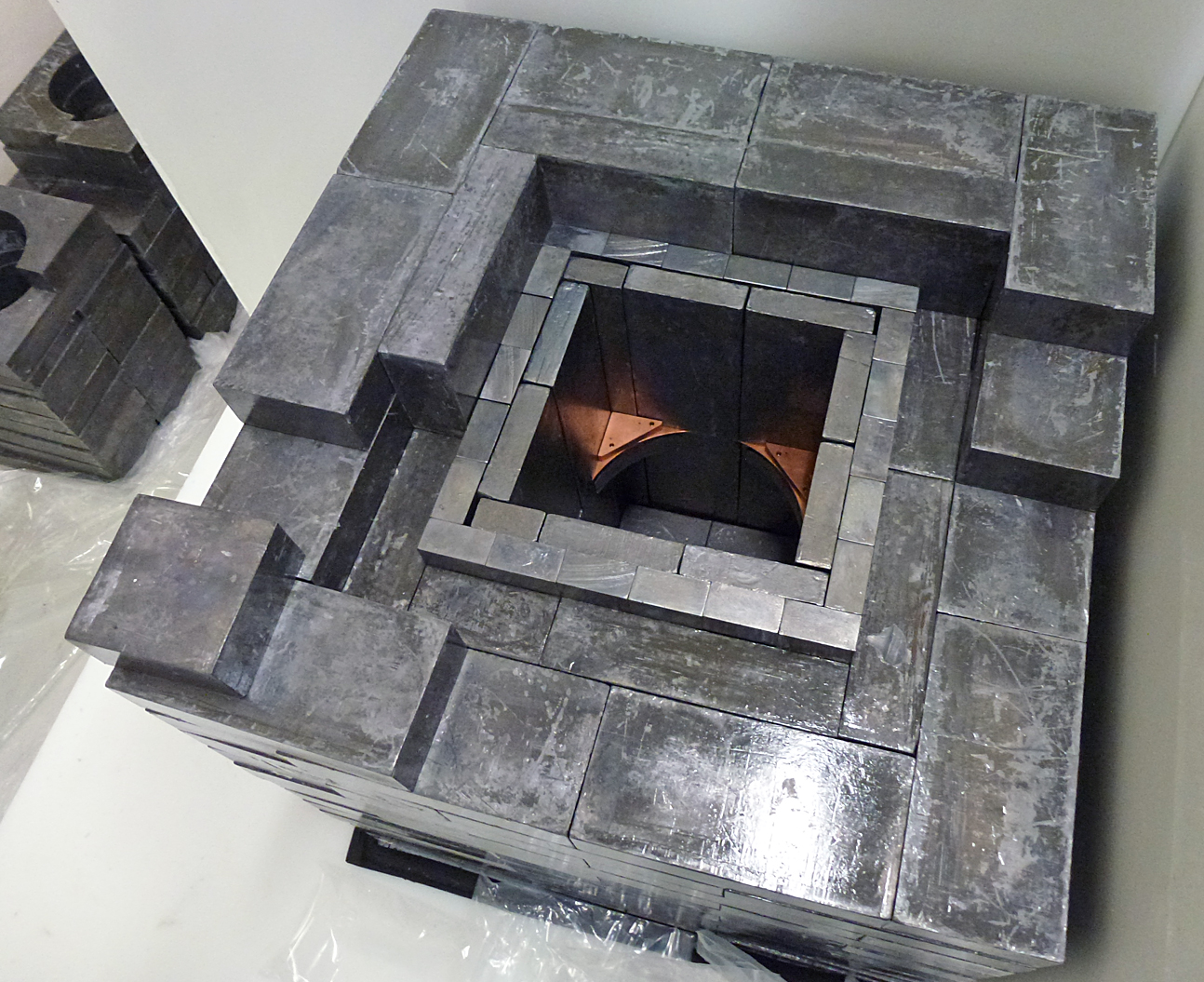
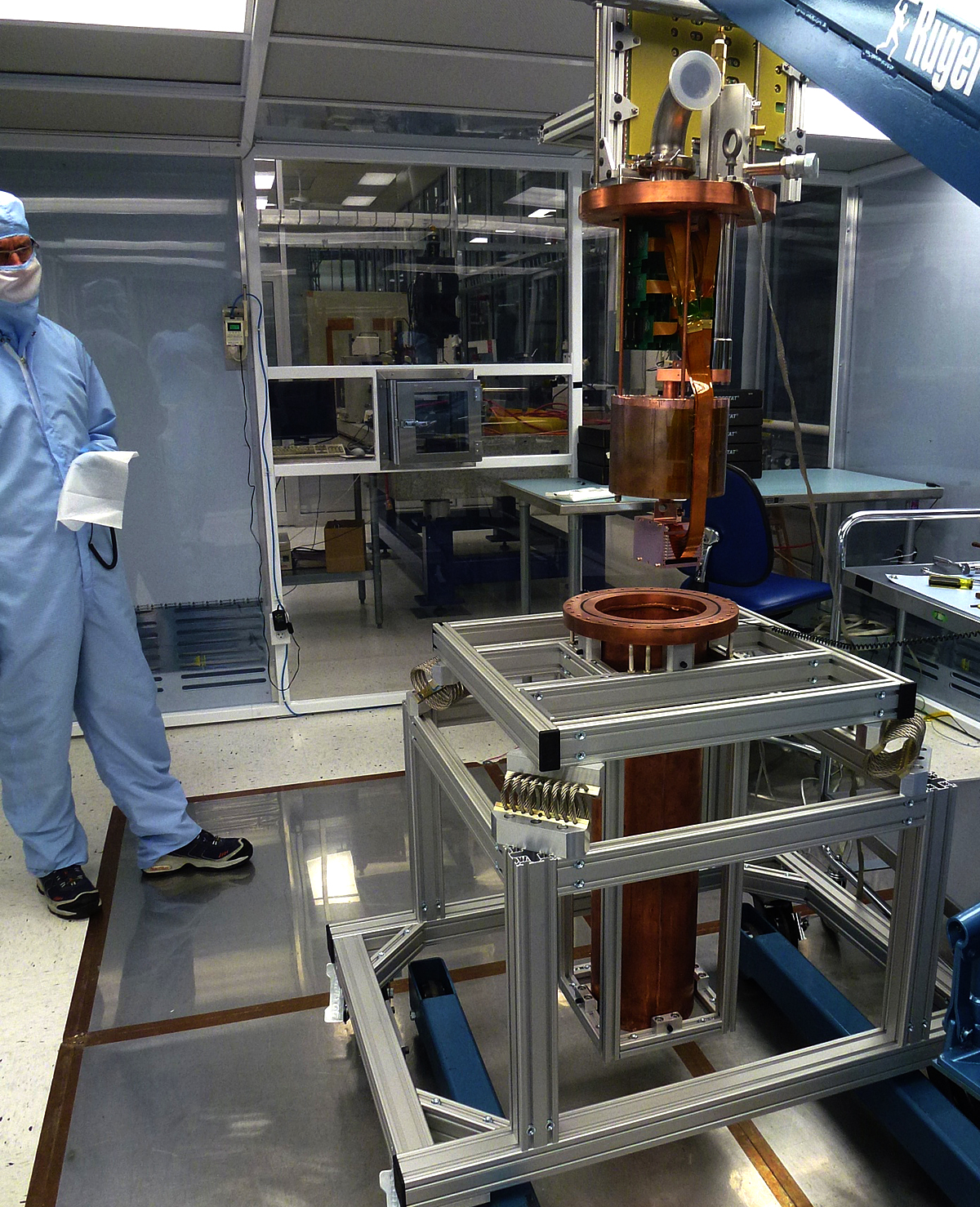
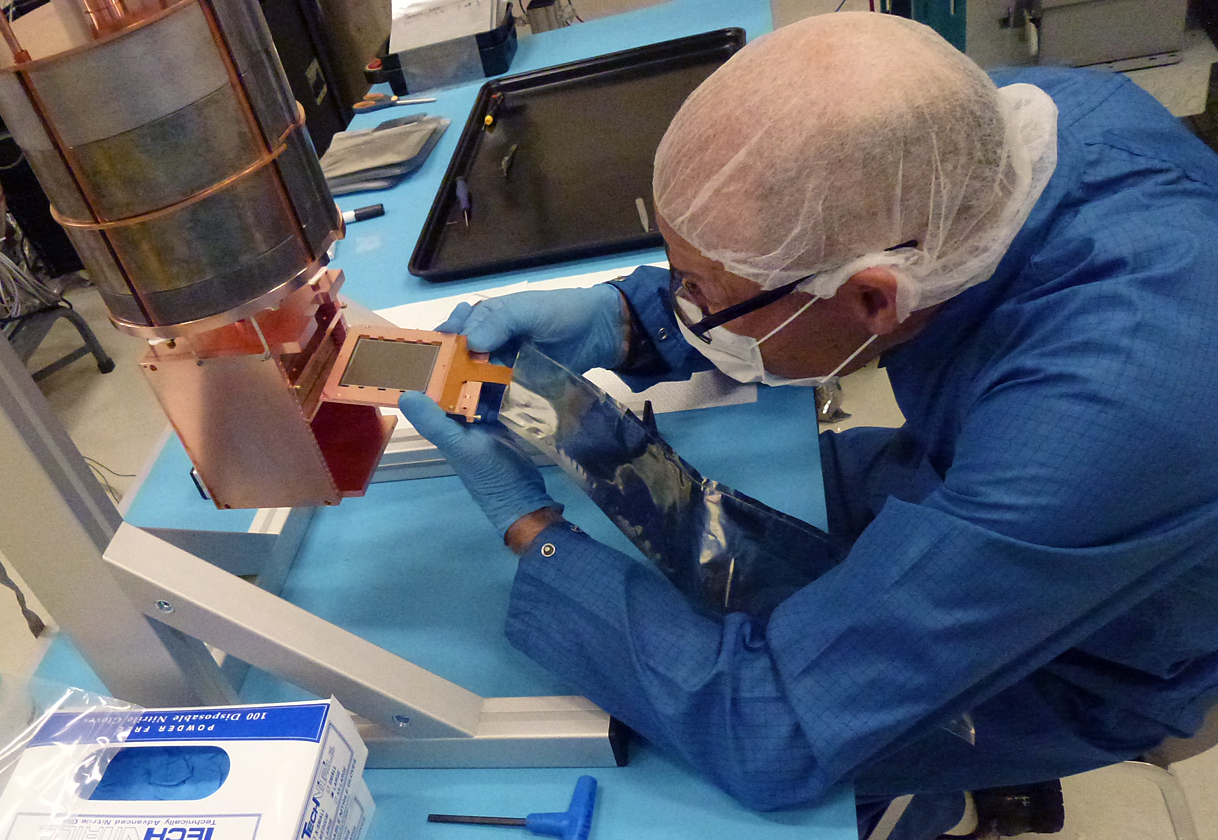
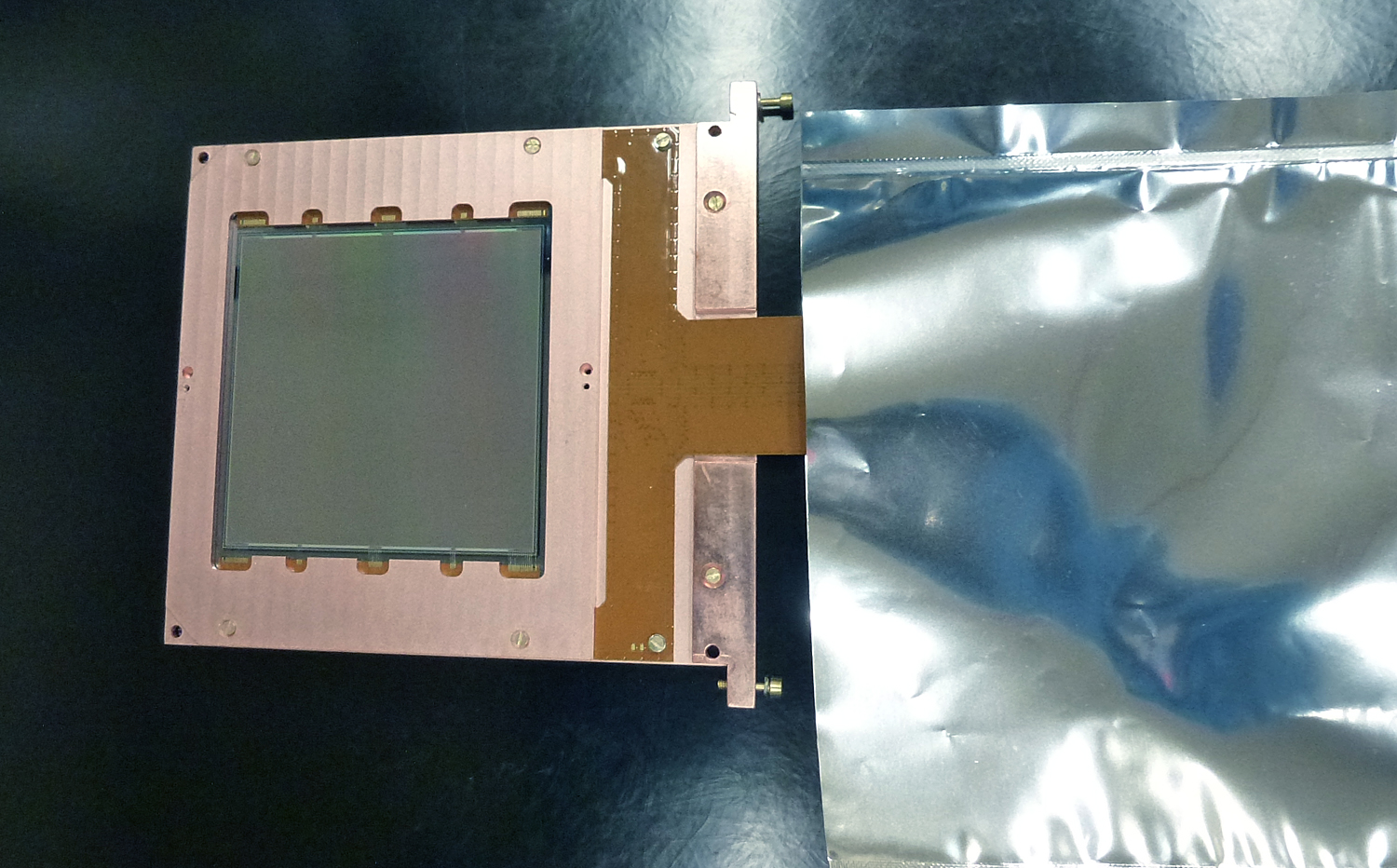
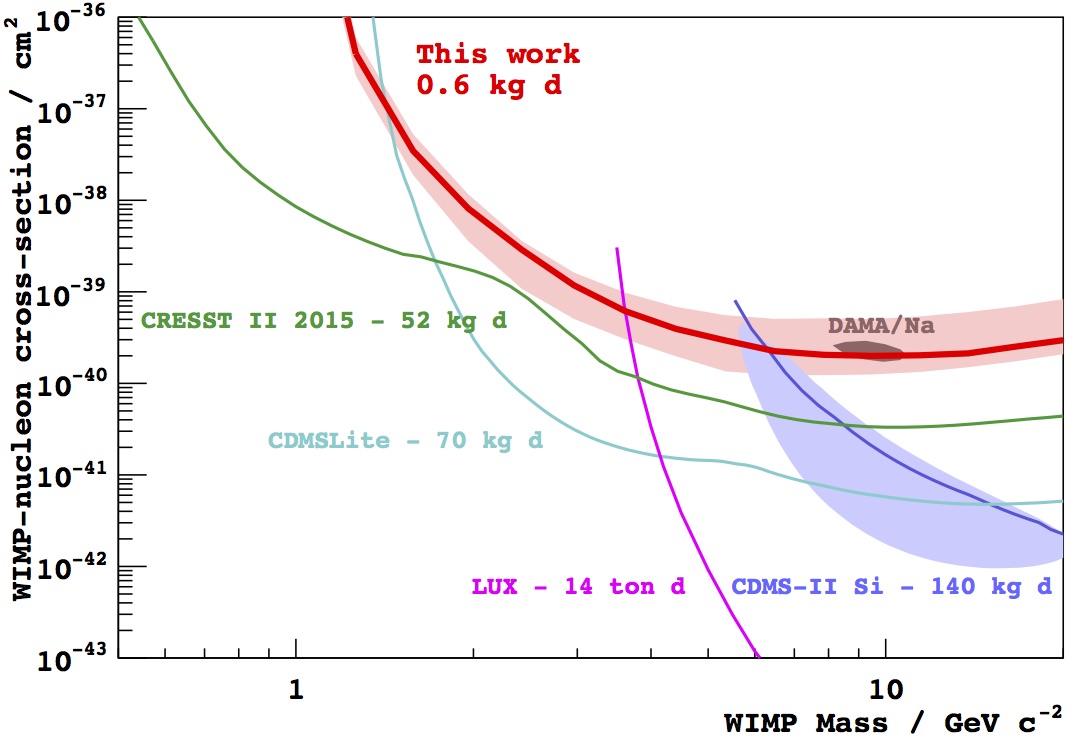
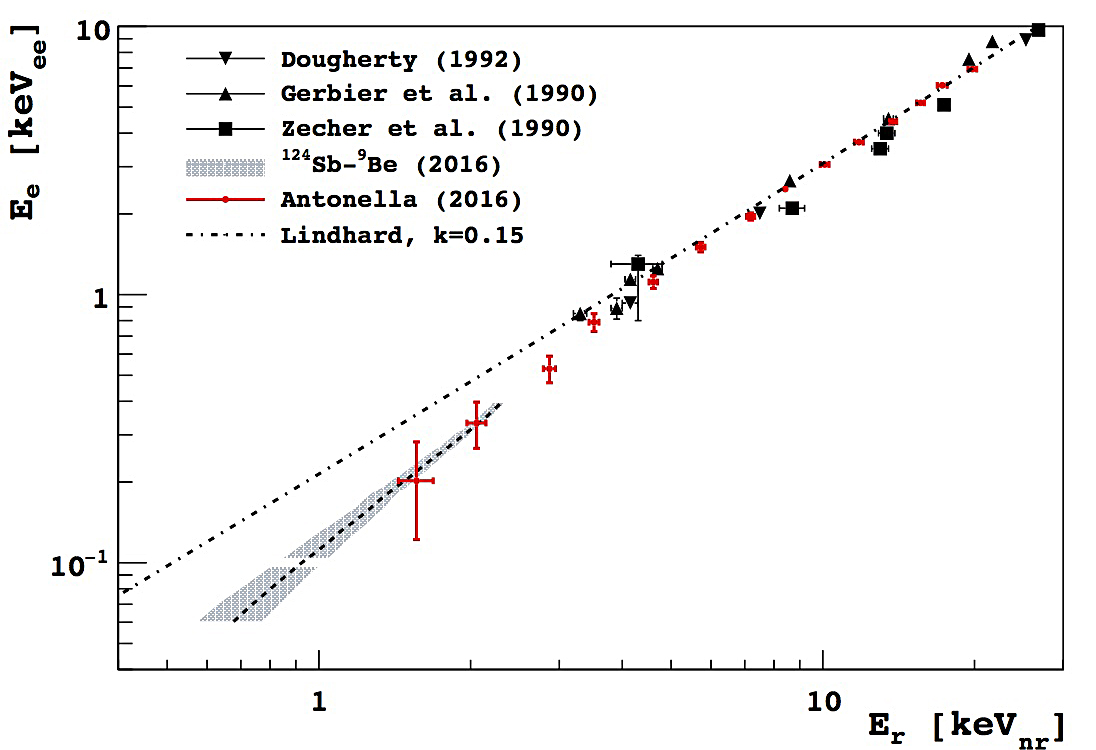
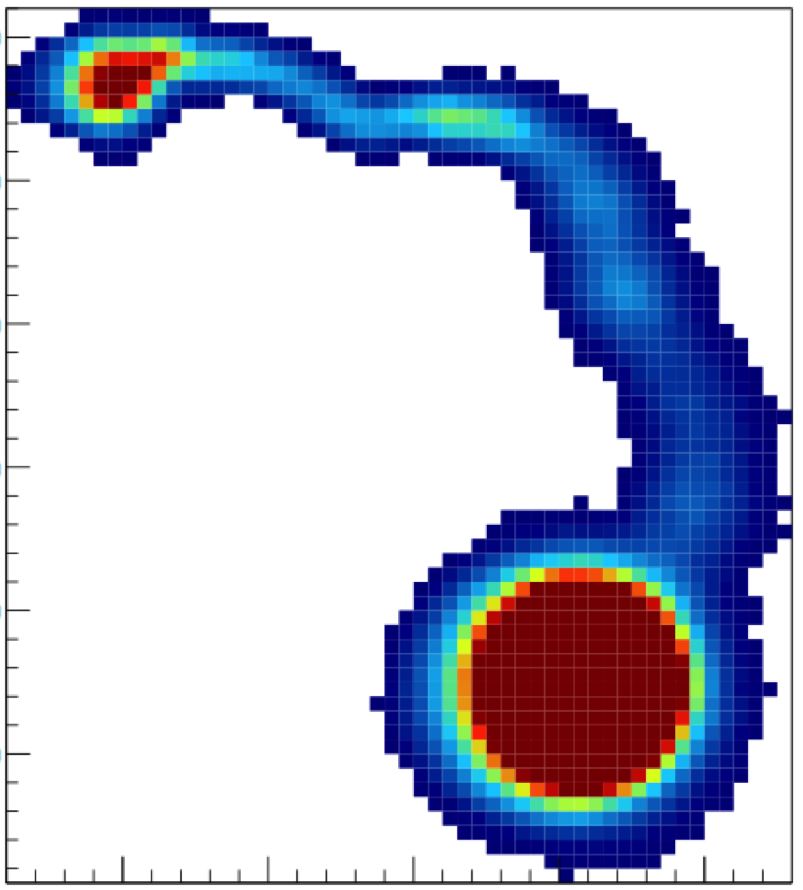
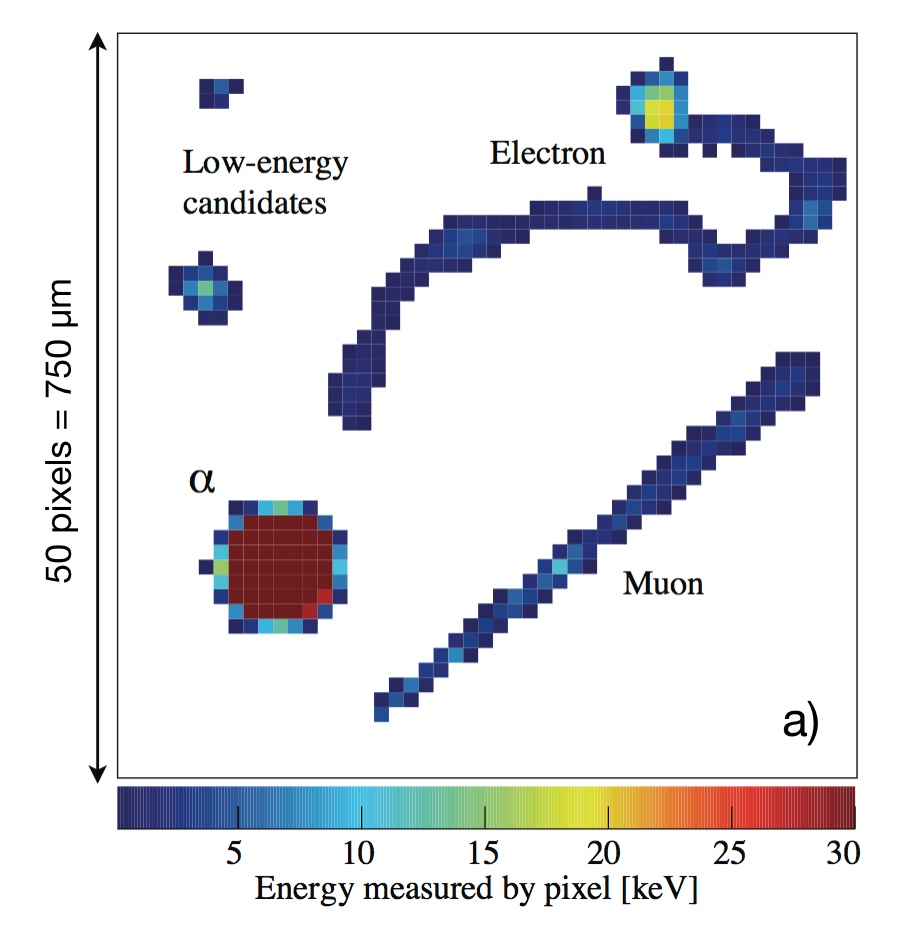
The WIMP cross-section σ χ−n September 11, 2016 Upper limit (90% C.L.) on the WIMP cross-section σ χ−n obtained with a small data set taken during DAMIC100 R&D phase (red line). Even if limited by the exposure and the level of radiogenic background — both to significantly improve in the upcoming DAMIC100 — these results demonstrate DAMIC’s sensitivity in the low-mass WIMP region (<10 GeV c−2), where the experiment is particularly competitive thanks to its low energy threshold.Learn more >> Measurement of the nuclear recoil ionization efficiency in Silicon September 9, 2016 The energy deposited into ionization, Ee, as a function of the nucleus recoil energy, Er. These are the first measurements of sub-keV nuclear recoils in Silicon.Learn more >> DAMIC installation at SNOLAB September 7, 2016 The copper vacuum vessel housing the CCDs is inserted in the lead shield. The DAMIC at SNOLAB lead shielding September 5, 2016 The innermost layer is made of ancient lead recovered from a sunken Spanish galleon and a Roman ship. The copper box hosting the CCDs September 3, 2016 The copper box hosting the CCDs, top lead shield and in-vacuum electronics being inserted in the copper vacuum vessel. DAMIC installation at SNOLAB September 1, 2016 A packaged CCD being inserted in the copper box. Above the box is a lead cylinder shielding the CCDs from radiogenic backgrounds. DAMIC is taking data at SNOLAB with 7 CCDs for a total mass of 40 g. An alpha and a beta particle originating from the same location in the CCD August 31, 2016 An alpha and a beta particle originating from the same location in the CCD, consistent with a nuclide from the Th chain undergoing subsequent decays. The excellent spatial resolution of the CCD provides a unique handle in the understanding of the radiogenic background. Particle identification by a DAMIC CCD August 29, 2016 A muon (straight track); an alpha particle (round blob); an electron (worm-like track) and low-energy particles (electrons from X rays or nuclear recoils). |